Embarking that elaborate overview involving man-made light cables (POF) reveals prominent upside in relation to prevailing silica optical ropes for targeted employments, primarily as a result of its enhanced durability and straightforwardness of installation. Its decreased outlay constitutes another crucial boon, rendering it apt for limited radius communication. POF customarily displays a enhanced core thickness, assisting simpler joining and lowering signal degradation. Nonetheless, when viewed against quartz fiberoptic wires, POF typically boasts a diminished channel and a elevated attenuation. Usual employments include home frameworks, automotive configurations, and short span industrial channels. Ongoing study focuses on strengthening POF’s range and curtailing its impairment to magnify its suitability in innovating platforms.
Radiant Fiber Lighting Fixture: Blueprint, Creation, and Glow
The alluring radiance of up-to-date fiber optic lanterns springs from a intriguing fusion of design principles, exacting forming methods, and the physics of light conveyance. Primarily, a light producer, often a miniature LED or halogen bulb, is merged into a bundle of exceptionally thin, pliable polymer fibers. These fibers, carefully organized, act as tiny light bearers, transmitting the dazzling radiation to the lamp’s exterior where it is dispersed to produce a gentle and spellbinding radiance. The organization of the fiber bundle, including density and positioning, directly influences the overall light configuration. Building involves meticulously bundling these fibers, frequently with reflective coatings to amplify light gathering. Ultimately, the resulting illumination presents a exclusive aesthetic – a soft climate that is both visually spectacular and surprisingly efficient.
Illuminated Costumes: Adopting Fiber Optics for Carryable Glow
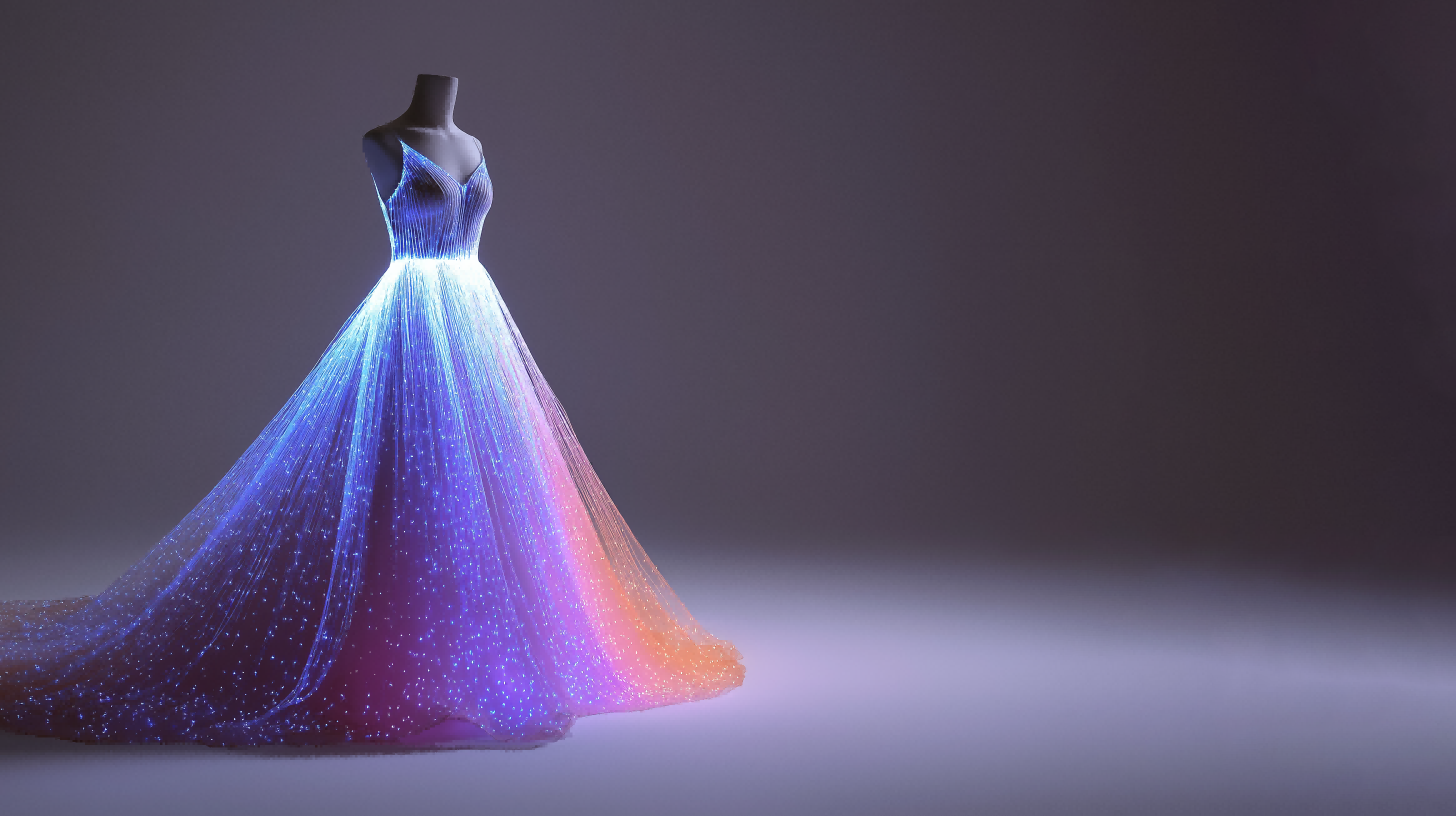
That fast field of hip development has ignited the fabrication of luminous clothing, a genuinely impressive confluence of textiles and optics. At its core resides the integration of fiber optics, microscopic strands of glass or plastic that direct light from an external source—typically a small, battery-powered LED—to produce dazzling and living visual effects straightaway on the garment. Envision a jacket that subtly shifts colors with your mobility, or a dress that pulses with a rhythmic, unearthly glow; these are merely a few examples of the opportunity furnished by this developing drift. The application extends far beyond mere aesthetics, however. Investigators are exploring uses in safety—imagine cyclists illuminated by fiber optic components—and even therapeutic deployments, wherein controlled light exposure may impart gains for specific conditions. The problem remains in crafting flexible, durable, and ultimately washable systems that can seamlessly meld into everyday apparel without sacrificing comfort or practicality, yet the future of illuminated textiles appears unequivocally promising.
Dissemination Optical Fiber: Information and Trustworthiness
A effectiveness of state-of-the-art signal architectures largely depends on the consistent passing of signals through optical radiant lines. Maintaining delivered accuracy during this method poses substantial barriers, especially as speed requirements escalate. Factors such as weakening, distribution, and complicated results degrade the signal, causing static and eventually limiting the feasible scope. Mitigation strategies, including advanced shaping schemes, signal spread control gadgets, and boosters, are vital for maintaining signal integrity and optimizing the performance of optical routes. Moreover, understanding directionality effects and utilizing polarization-control threads are critical for certain purposes, assuring a dependable relationship.
Polymer Optical Fiber Illumination Setups: Extensive Presentation
Understanding Polymer Fiber lighting frameworks is growing in necessity as energy efficiency gains steam. A study delivers a in-depth review of the technology, encompassing everything from core principles to applicable functions. Users realize the strengths of incorporating Polymer Fiber – including its toughness, straightforwardness of implementation, and promise for decreased voltage utilization. Additionally, we address common hurdles and review the potential of this developing lighting industry.
Optical Fiber Textiles: Fabricating Living and Tailored Apparel
The developing field, fiber optic textiles is upgrading garments design, initiating an era of responsive and customized garments. These novel creations effortlessly merge light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, promptly within the composition of the textile, enabling the manufacture of spectacular visual effects. Envision a outfit that transforms color according to the wearer’s mood, or a overcoat displaying real-time news from a connected device. The potential for aesthetic communication and functional application is broad, stretching from show costumes to preventive gear and even engaging art presentations. This linkage of woven science and digital technology heralds a future wherein our attire becomes a effective form of transmission.
Luminous Thread Communication: Parameters and Advanced Trends
Optical strand communication constitutes a crucial innovation for data information transfer, exploiting the principles of total internal mirroring within a slender, pliable silica core. Originally, systems relied on direct modulation of light intensity, but contemporary advancements, such as rhythm modulation and coherent detection, markedly strengthen spectral efficiency and extent. The recent advancements comprise spatial division combining, which multiplies efficiency by harnessing several spatial modes within the cord, along with the expanding field of few-mode luminous line systems delivering a adjustment between performance and expenditure. Further exploration targets advancing chaotic compensation strategies that lessen impairments created by the fiber itself, alongside probing uncommon materials, like hollow-core optic filament, to accomplish even greater data rates and enlarge the scope of operationalities.
Polymer Optical Fiber Sensors: Detection and Determination
Polymer Optical Thread fibers are increasingly exploited for sensing various measures due to their resilience, thriftiness, and effortlessness of incorporation. The sensing procedure often entails a change in intensity of the carried light, elicited by the target being sensed. These variations can be scrutinized using standard optoelectronic systems which adapt the light outputs into electronic signals for subsequent interpretation. Unique monitor designs apply a variety of approaches, such as reflective impedance observation, optic Bragg gratings, or boundary plasmon resonance, to amplify the exactness and variable range of the complete system.
Radiant Displays: Harnessing Fiber Optics for Optical Effects
This engaging look of fiber optic lighting is uncovering increasingly imaginative uses in the domain of visual displays. Rather than conventional lighting methods, artists and designers are harnessing the characteristics of fiber optics to craft truly breathtaking and adaptive effects. Picture a sculpture that seems to sparkle from inside, or a building exterior that subtly changes color and intensity—these examples illustrate just part of what’s achievable. The individual fibers, often exceedingly slim, act as light directions, delivering illumination to precisely appointed points, enabling intricate patterns and designs. This grants a degree of control and a distinctive visual aspect simply unattainable with traditional lighting systems, pushing the boundaries of architectural and artistic exhibition.
State-of-the-Art Optical Filament Materials and Manufacturing
Its improvement of superior optical fiber critically depends on both recent materials and precisely controlled creation processes. Traditionally, silica-based glass have dominated, yet achieving the imperative ultra-low reduction and high volume mandates doping with elements such as germanium, phosphorus, or fluorine, precisely adjusted at the molecular level. Further research increasingly emphasizes alternative elements like chalcogenide forms and even lattice-based configurations displaying elevated optical traits. Fabrication methods span traditional modified chemical vapor deposition (MCVD) to more state-of-the-art techniques like vapor phase infiltration (VPI) and laser-induced forward transfer (LIFT), each necessitating extremely stringent ranges on diameter, refractive ratio profiles, and dynamic uniformity. Flaw detection during manufacturing remains paramount for assuring extended durability and minimizing signal deterioration.
Luminous Fiber Art: Installations and Exhibits
Surpassing established artistic approaches, a fascinating discipline is materializing: fiber optic art. This innovative practice admits strands of glass fiber to construct breathtaking works and immersive backgrounds. Artists take advantage of the extraordinary properties of light transmission, engendering luminous effects that transform space and engage the viewer. From delicate miniature forms to large-scale, interactive environments that envelop the senses, fiber optic art provides a groundbreaking perspective on light, form, and expressive beauty. The promise for exploration within this fairly new artistic space is substantial, promising a continuing evolution of its modalities and revelations.
 optical fiber decoration
optical fiber decoration